Rebound O&P
Updated 12:04 PM CDT, Mon March 10, 2025
Published Under: Orthotics
Osteoarthritis (OA) is one of the most common forms of arthritis, particularly affecting the knee joint. As a degenerative condition, it involves the breakdown of cartilage, the tissue that cushions the ends of bones in the joint. This blog will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for osteoarthritis in the knee, helping you understand this condition and how to manage it effectively.
What is Osteoarthritis?
Osteoarthritis is a chronic condition that leads to the gradual deterioration of cartilage, resulting in pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility in the affected joints. While it can occur in any joint, the knee is particularly susceptible due to the weight-bearing nature of this joint and its role in movement.
Causes of Osteoarthritis in the Knee
Several factors can contribute to the development of osteoarthritis in the knee:
- Age: As we age, the cartilage in our joints naturally wears down, making older adults more susceptible to OA.
- Obesity: Excess weight places additional stress on weight-bearing joints like the knees, accelerating cartilage breakdown.
- Previous Injuries: Injuries to the knee, such as fractures or ligament tears, can increase the risk of developing OA later in life.
- Genetics: A family history of osteoarthritis can increase the likelihood of developing the condition.
- Overuse: Repetitive stress on the knee joint from certain occupations or athletic activities can contribute to cartilage wear.
- Joint Alignment: Abnormalities in joint structure, such as misalignment or bowing of the legs, can put extra pressure on certain areas of the knee.
Symptoms of Osteoarthritis in the Knee
The symptoms of knee osteoarthritis can vary in severity and may include:
- Pain: This is often the first symptom, usually worsening with activity and improving with rest.
- Stiffness: You may experience stiffness in the knee, especially after sitting for long periods or upon waking.
- Instability: There may be moments where the knee buckles or gives when walking that may cause you to stumble or fall.
- Swelling: Inflammation in the joint can lead to noticeable swelling.
- Decreased Range of Motion: You might find it difficult to fully bend or straighten your knee.
- Creaking or Grating Sounds: A sensation of grating or popping when moving the knee can occur due to roughened cartilage.
- Joint Deformities: In advanced cases, the knee may appear misshapen or swollen.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing osteoarthritis typically involves several steps:
- Medical History: Your healthcare provider will ask about your symptoms, medical history, and any previous injuries.
- Physical Examination: A thorough examination of your knee will help assess swelling, pain, and range of motion.
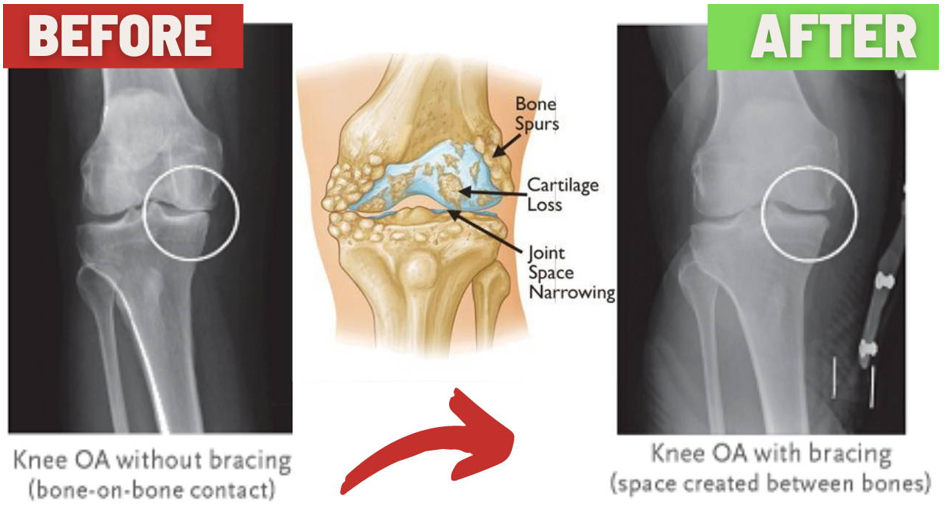
- Imaging Tests: X-rays can show changes in the joint, such as cartilage loss, bone spurs, and joint space narrowing. In some cases, MRI may be used for a more detailed view of the cartilage and soft tissues.
- Laboratory Tests: While there are no specific blood tests for OA, your doctor may conduct tests to rule out other types of arthritis.
Treatment Options
While there is no cure for osteoarthritis, various treatment options can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life:
1. Lifestyle Modifications
- Weight Management: Losing excess weight can significantly reduce pressure on the knees and alleviate pain.
- Physical Activity: Low-impact exercises such as swimming, cycling, and walking can help strengthen muscles around the knee and improve flexibility.
2. Physical Therapy
Working with a physical therapist can provide tailored exercises to strengthen the knee and improve range of motion, helping to alleviate pain and enhance functionality.
3. Medications
- Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter medications like acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help manage pain and reduce inflammation.
- Topical Treatments: Creams containing analgesics or capsaicin can provide localized relief.
4. Injections
- Corticosteroid Injections: These can provide temporary relief from inflammation and pain.
- Hyaluronic Acid Injections: These may help lubricate the joint and improve mobility.
Braces, canes, or shoe inserts can help reduce stress on the knee and improve stability while walking.
6. Surgical Options
If conservative treatments fail and symptoms significantly impact daily life, surgical options may be considered:
- Arthroscopy: A minimally invasive procedure to clean out the joint.
- Osteotomy: Adjusting the alignment of the bones to relieve pressure on the knee.
- Knee Replacement: Partial or total knee replacement may be recommended in advanced cases.
Conclusion
Osteoarthritis in the knee can be a challenging condition, but understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options can empower you to take control of your health. By adopting a proactive approach that includes lifestyle modifications, physical therapy, and medical interventions, you can effectively manage symptoms and maintain an active lifestyle. If you suspect you have knee osteoarthritis, consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and a personalized treatment plan. Remember, early intervention can make a significant difference in your journey toward improved mobility and quality of life!

Comments